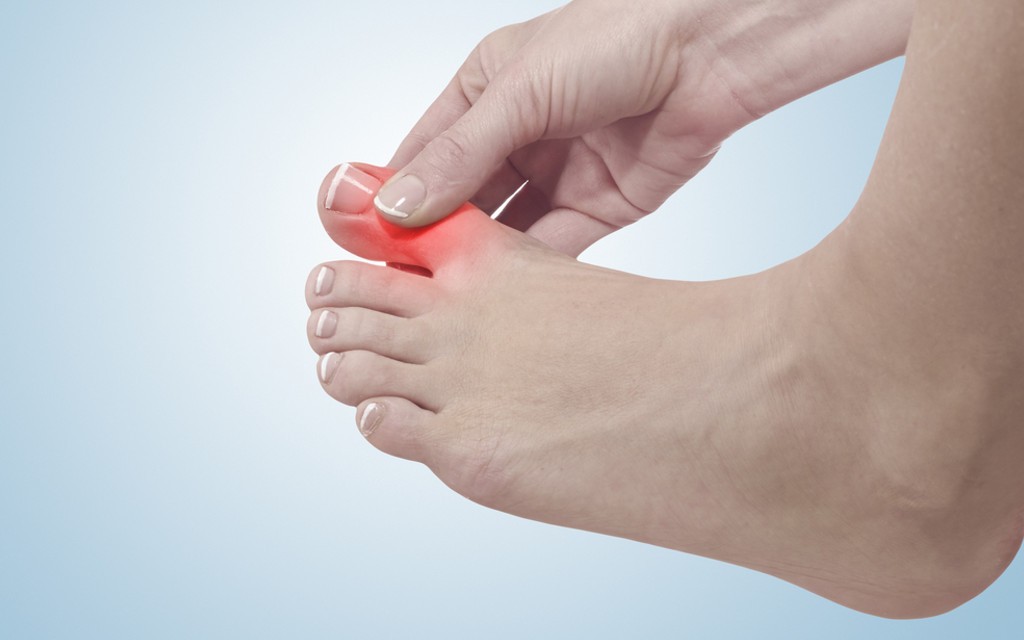
Gout: Its causes, symptoms, and risk factors
Gout is a type of arthritis that leads to painful inflammation in a joint. Small crystals form in and around the joint, causing inflammation, pain and swelling. These crystals are made of one of the body’s normal waste products, uric acid. Normally the body rids itself of extra uric acid through the kidneys into the urine. However this does not happen fast enough in people with gout. This causes uric acid levels to build up as well as crystals to form. The big toe is most commonly affected, but gout can affect the hands, wrists, knees, ankles, elbows or any other joint.
It generally develops earlier in men (often between 30 and 45 years) than in women (usually after age 55). And it’s common in people over 65 regardless of their gender.
What are the symptoms of gout?
The symptoms of gout include:
- pain in a joint, which can be quite severe
- swelling around the joint, which feels tender – even through clothing
- warmth and redness of the skin over the affected joint
- restricted movement of the joint
These symptoms usually develop rapidly and can last for 1 to 2 weeks.
Causes of Gout
Gout is usually caused by your kidneys not flushing uric acid out of your body quickly enough. It runs in families, although not all family members will be affected. There are some lifestyle factors which may increase your risk of developing gout, including:
- being overweight or obese
- having high cholesterol, high blood pressure or glucose intolerance
- having kidney disease
- taking diuretics (tablets that drain water from the body)
Early diagnosis and treatment is very important. The main goal for everyday management of gout is to reduce the level of uric acid in your blood so it can’t form crystals in the tissues or joints and cause joint damage.
Are you suffering from this condition? One of our podiatrist can assist and recommend what treatment options are best to get you back on track. ✅
Schedule an appointment here or you may call us at 44 (0) 207 101 4000. 📞
We hope you have a feetastic day! 👣☀️
-The Chelsea Clinic and Team